Custom tools
Learn more about creating custom tools for your agents.
Build conversational assistants that store memories in MongoDB, Graphiti, Weaviate, Mem0, or Zep with complete control over memory storage and retrieval.
By default, Letta agents store memories in Letta’s built-in storage system. However, you can integrate external memory providers to store and retrieve agent memories in your own infrastructure. This gives you complete control over memory storage, search capabilities, and data persistence.
In this guide, we’ll build a conversational assistant that stores its memories in external databases. We’ll implement custom tools for five different memory providers: MongoDB, Graphiti, Weaviate, Mem0, and Zep.
To follow this tutorial, you need:
You also need API keys for Letta and your chosen memory provider.
Create a Letta Account
If you don’t have one, sign up for a free account at letta.com.
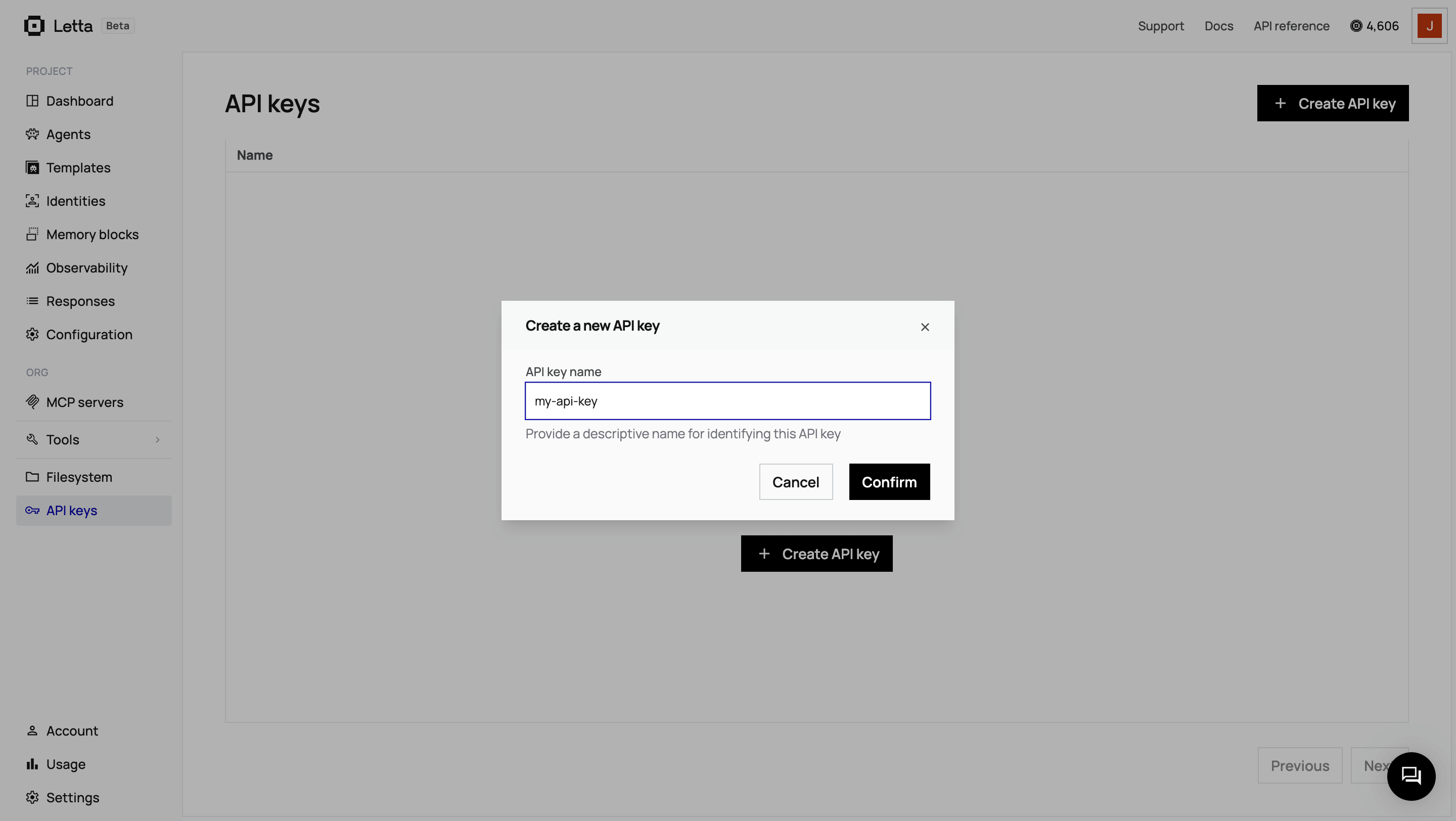
Navigate to API keys
Once logged in, click on API keys in the sidebar.
Create and copy your key
Click + Create API key, give it a descriptive name, and click Confirm. Copy the key and save it somewhere safe.
mongodb+srv://<username>:<password>@cluster0.xxxxx.mongodb.net/?retryWrites=true&w=majority&appName=Cluster0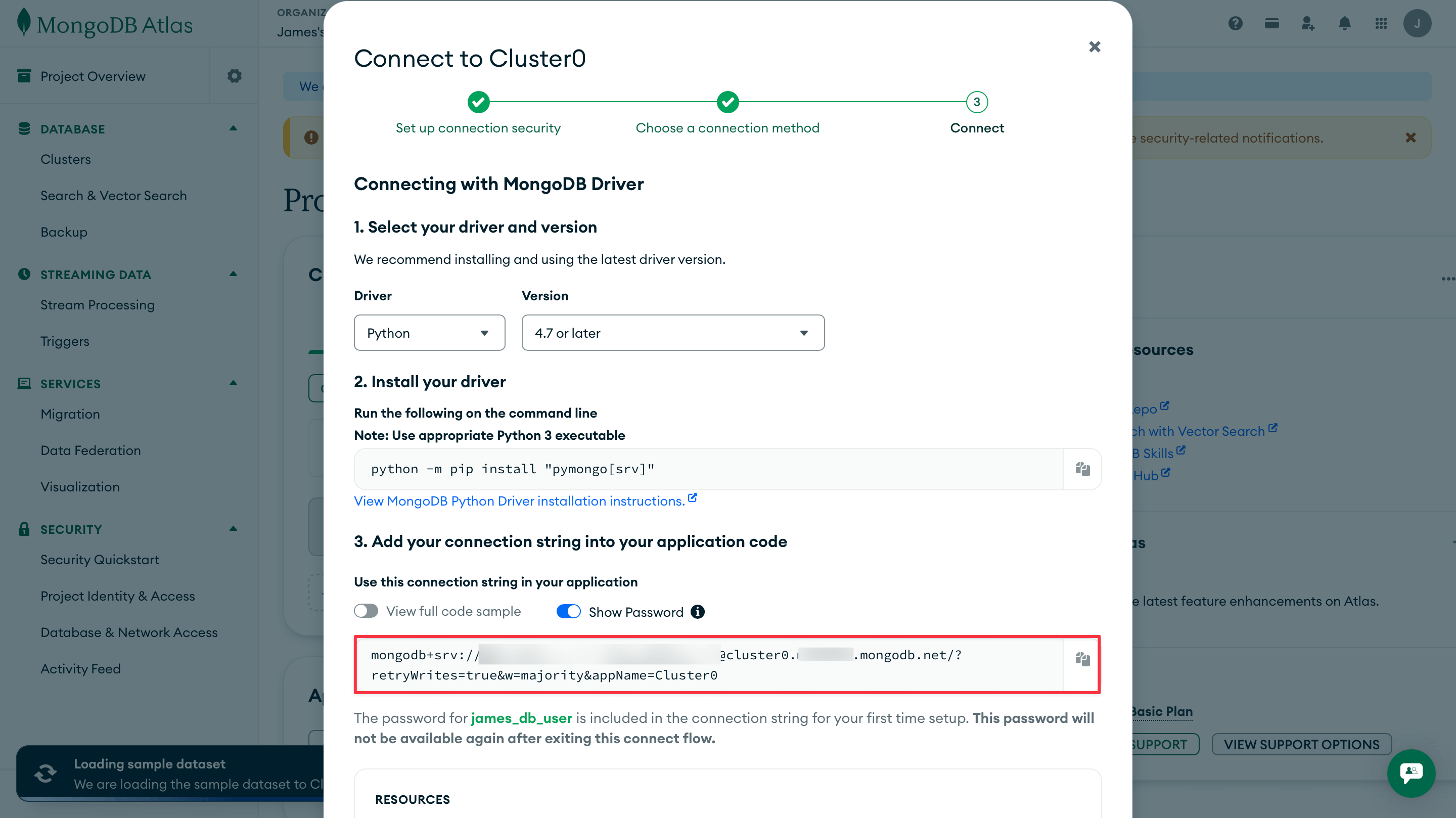
0.0.0.0/0.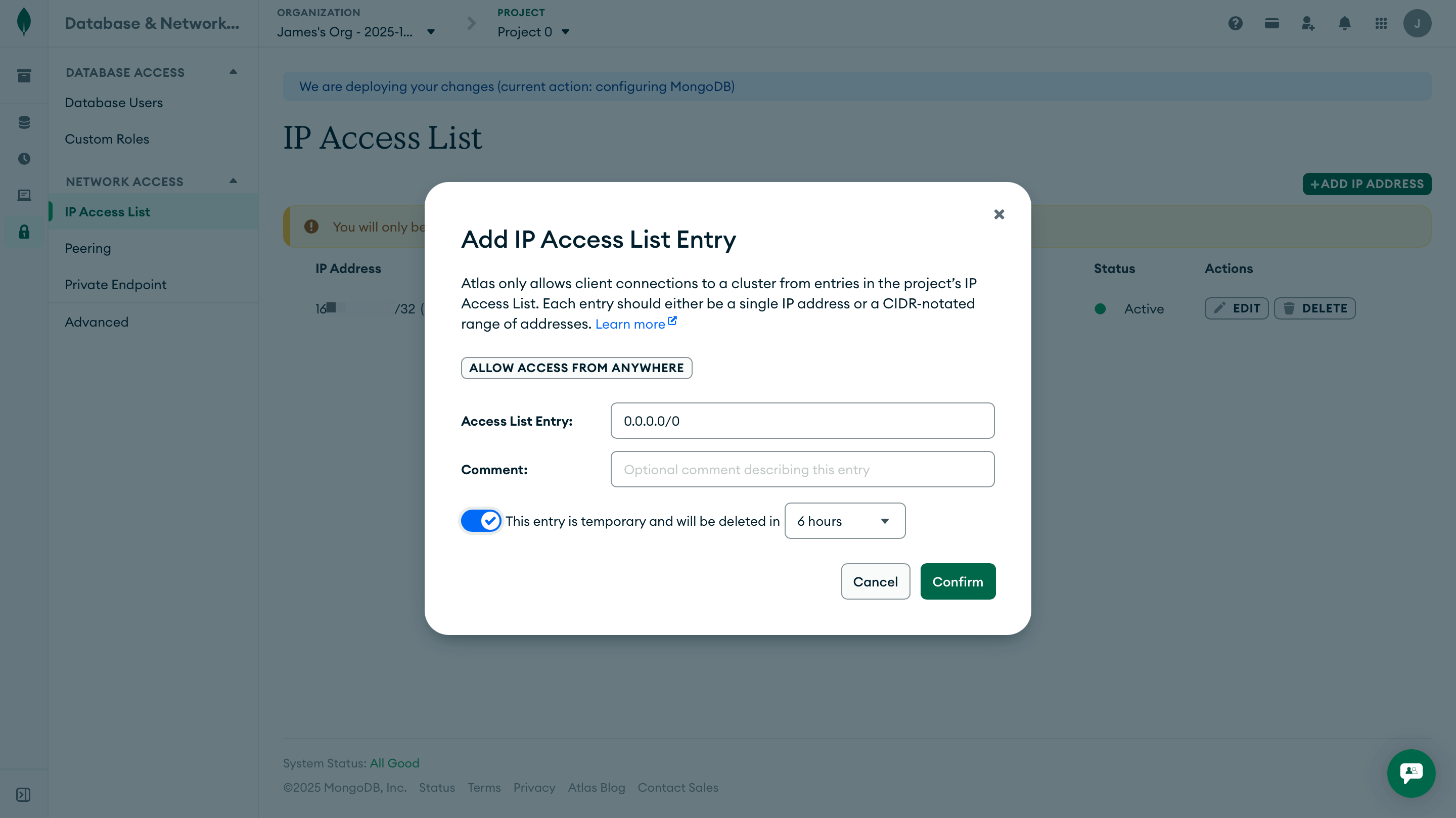
neo4j (default)
neo4j+s://<instance-id>.databases.neo4j.ioFor example, if your instance ID is abc12345, your URI would be neo4j+s://abc12345.databases.neo4j.io.
https://xxxxx.weaviate.cloud
z_).
Once you have these credentials, create a .env file in your project directory and save them as environment variables:
LETTA_API_KEY="..."MONGODB_URI="mongodb+srv://username:password@cluster0.xxxxx.mongodb.net/?retryWrites=true&w=majority&appName=Cluster0"MONGODB_DB_NAME="letta_memories"LETTA_API_KEY="..."OPENAI_API_KEY="..."NEO4J_URI="neo4j+s://xxxxx.databases.neo4j.io"NEO4J_USER="neo4j"NEO4J_PASSWORD="..."LETTA_API_KEY="..."WEAVIATE_URL="https://xxxxx.weaviate.cloud"WEAVIATE_API_KEY="..."OPENAI_API_KEY="..."LETTA_API_KEY="..."MEM0_API_KEY="..."LETTA_API_KEY="..."ZEP_API_KEY="z_..."First, we need to prepare the external database to store agent memories. Each provider requires different setup steps.
Before you begin, set up your development environment:
# Create a Python virtual environment to keep dependencies isolatedpython -m venv venvsource venv/bin/activate # On Windows, use: venv\Scripts\activateCreate a requirements.txt file that lists the necessary packages for your chosen provider:
letta-clientpymongocertifidnspythonpython-dotenvInstall the packages with the following command:
pip install -r requirements.txtletta-clientgraphiti-core[neo4j]python-dotenvInstall the packages with the following command:
pip install -r requirements.txtletta-clientweaviate-client>=4.0.0python-dotenvInstall the packages with the following command:
pip install -r requirements.txtletta-clientmem0aipython-dotenvInstall the packages with the following command:
pip install -r requirements.txtletta-clientzep-cloud>=3.0.0python-dotenvInstall the packages with the following command:
pip install -r requirements.txt# Initialize a new Node.js project if you haven't alreadynpm init -y
# Create tsconfig.json for TypeScript configurationcat > tsconfig.json << 'EOF'{ "compilerOptions": { "target": "ES2020", "module": "ESNext", "moduleResolution": "node", "esModuleInterop": true, "skipLibCheck": true, "strict": true }}EOFUpdate package.json to use ES modules:
"type": "module"Install the necessary packages for your chosen provider:
npm install @letta-ai/letta-client mongodb dotenvnpm install --save-dev typescript @types/node tsxnpm install @letta-ai/letta-client dotenvnpm install --save-dev typescript @types/node tsxnpm install @letta-ai/letta-client weaviate-client dotenvnpm install --save-dev typescript @types/node tsxnpm install @letta-ai/letta-client mem0ai dotenvnpm install --save-dev typescript @types/node tsxnpm install @letta-ai/letta-client @getzep/zep-cloud dotenvnpm install --save-dev typescript @types/node tsxIf your provider requires you to set up the infrastructure, initialize your database with the following code:
Create a setup.py or setup.ts file to add the code:
import osimport pymongoimport certififrom dotenv import load_dotenv
load_dotenv()
def main(): mongodb_uri = os.getenv("MONGODB_URI") db_name = os.getenv("MONGODB_DB_NAME")
if not all([mongodb_uri, db_name]): print("Error: MONGODB_URI and MONGODB_DB_NAME not set") return
print("Connecting to MongoDB...") client = pymongo.MongoClient(mongodb_uri, tlsCAFile=certifi.where())
db = client[db_name] collection = db["agent_memories"]
print("Creating indexes...") collection.create_index("agent_id") collection.create_index("user_id") collection.create_index([("agent_id", pymongo.ASCENDING), ("timestamp", pymongo.DESCENDING)]) collection.create_index([("memory_text", "text")])
print(f"\nSetup complete!") print(f"Database: {db_name}") print(f"Collection: agent_memories")
client.close()
if __name__ == "__main__": main()import { MongoClient } from 'mongodb';import dotenv from 'dotenv';
dotenv.config();
async function main() { const mongodbUri = process.env.MONGODB_URI; const dbName = process.env.MONGODB_DB_NAME;
if (!mongodbUri || !dbName) { console.error('Error: MONGODB_URI and MONGODB_DB_NAME not set'); return; }
console.log('Connecting to MongoDB...'); const client = new MongoClient(mongodbUri);
try { await client.connect(); const db = client.db(dbName); const collection = db.collection('agent_memories');
console.log('Creating indexes...'); await collection.createIndex({ agent_id: 1 }); await collection.createIndex({ user_id: 1 }); await collection.createIndex({ agent_id: 1, timestamp: -1 }); await collection.createIndex({ memory_text: 'text' });
console.log('\nSetup complete!'); console.log(`Database: ${dbName}`); console.log('Collection: agent_memories'); } finally { await client.close(); }}
main().catch(console.error);Run the setup script:
python setup.pynpx tsx setup.tsimport osimport asynciofrom graphiti_core import Graphitifrom dotenv import load_dotenv
load_dotenv()
async def main(): neo4j_uri = os.getenv("NEO4J_URI") neo4j_user = os.getenv("NEO4J_USER") neo4j_password = os.getenv("NEO4J_PASSWORD")
if not all([neo4j_uri, neo4j_user, neo4j_password]): print("Error: Neo4j credentials not set") return
print("Connecting to Neo4j...") graphiti = Graphiti(neo4j_uri, neo4j_user, neo4j_password)
try: print("Building indices and constraints...") await graphiti.build_indices_and_constraints() print("\nSetup complete!") except Exception as e: print(f"Error: {str(e)}") finally: await graphiti.close()
if __name__ == "__main__": asyncio.run(main())Run the setup script:
python setup.pyimport osimport weaviatefrom weaviate.classes.init import Authfrom weaviate.classes.config import Configure, Property, DataTypefrom dotenv import load_dotenv
load_dotenv()
def main(): weaviate_url = os.getenv("WEAVIATE_URL") weaviate_api_key = os.getenv("WEAVIATE_API_KEY") openai_api_key = os.getenv("OPENAI_API_KEY")
if not all([weaviate_url, weaviate_api_key, openai_api_key]): print("Error: Missing Weaviate or OpenAI credentials") return
try: print("Connecting to Weaviate...") client = weaviate.connect_to_weaviate_cloud( cluster_url=weaviate_url, auth_credentials=Auth.api_key(weaviate_api_key), headers={"X-OpenAI-Api-Key": openai_api_key} )
if client.collections.exists("AgentMemory"): print("AgentMemory collection already exists") response = input("Delete and recreate? (yes/no): ").lower() if response == "yes": client.collections.delete("AgentMemory") else: client.close() return
print("Creating AgentMemory collection...") client.collections.create( name="AgentMemory", vector_config=Configure.Vectors.text2vec_openai( model="text-embedding-3-small" ), properties=[ Property(name="memory_text", data_type=DataType.TEXT), Property(name="agent_id", data_type=DataType.TEXT), Property(name="user_id", data_type=DataType.TEXT), Property(name="created_at", data_type=DataType.TEXT) ] )
print("\nSetup complete!") print("Collection: AgentMemory") client.close()
except Exception as e: print(f"Error: {str(e)}") raise
if __name__ == "__main__": main()import weaviate, { WeaviateClient, configure } from 'weaviate-client';import dotenv from 'dotenv';import * as readline from 'readline';
dotenv.config();
async function askQuestion(query: string): Promise<string> { const rl = readline.createInterface({ input: process.stdin, output: process.stdout, });
return new Promise((resolve) => { rl.question(query, (answer) => { rl.close(); resolve(answer); }); });}
async function main() { const weaviateUrl = process.env.WEAVIATE_URL; const weaviateApiKey = process.env.WEAVIATE_API_KEY; const openaiApiKey = process.env.OPENAI_API_KEY;
if (!weaviateUrl || !weaviateApiKey || !openaiApiKey) { console.error('Error: Missing Weaviate or OpenAI credentials'); return; }
try { console.log('Connecting to Weaviate...'); const client: WeaviateClient = await weaviate.connectToWeaviateCloud(weaviateUrl, { authCredentials: new weaviate.ApiKey(weaviateApiKey), headers: { 'X-OpenAI-Api-Key': openaiApiKey }, });
const exists = await client.collections.exists('AgentMemory');
if (exists) { console.log('AgentMemory collection already exists'); const response = await askQuestion('Delete and recreate? (yes/no): '); if (response.toLowerCase() === 'yes') { await client.collections.delete('AgentMemory'); } else { await client.close(); return; } }
console.log('Creating AgentMemory collection...'); await client.collections.create({ name: 'AgentMemory', vectorizers: weaviate.configure.vectorizer.text2VecOpenAI({ model: 'text-embedding-3-small', }), properties: [ { name: 'memory_text', dataType: 'text' }, { name: 'agent_id', dataType: 'text' }, { name: 'user_id', dataType: 'text' }, { name: 'created_at', dataType: 'text' }, ], });
console.log('\nSetup complete!'); console.log('Collection: AgentMemory'); await client.close(); } catch (error) { console.error(`Error: ${error}`); throw error; }}
main().catch(console.error);Run the setup script:
python setup.pynpx tsx setup.tsNo setup required! Mem0 is a fully managed service and will automatically store and organize your memories when you use the memory tools in Step 2.
Proceed directly to Step 2 to create your memory tools.
No setup required! Zep is a fully managed service and will automatically store and organize your memories when you use the memory tools in Step 2.
Proceed directly to Step 2 to create your memory tools.
A Letta tool is a Python function that your agent can call. We’ll create two tools for each provider:
insert_memory: Stores new memories with agent ID, user ID, and contentsearch_memory: Retrieves relevant memories filtered by agent and userLetta automatically generates JSON schemas from your function signatures and docstrings, making these tools available to your agent. The agent can then decide when to call these functions based on the conversation.
Create a new file named tools.py or tools.ts with the implementation for your chosen provider:
import os
def insert_memory(memory_text: str, memory_agent_id: str, user_id: str = "default_user") -> str: """ Store a memory in MongoDB for a specific agent and user.
Args: memory_text: The memory content to store memory_agent_id: The ID of the agent storing this memory user_id: The ID of the user this memory relates to
Returns: Confirmation message with the inserted memory ID """ import pymongo import certifi from datetime import datetime
try: mongodb_uri = os.getenv("MONGODB_URI") db_name = os.getenv("MONGODB_DB_NAME")
if not all([mongodb_uri, db_name]): return "Error: MongoDB credentials not configured"
client = pymongo.MongoClient(mongodb_uri, tlsCAFile=certifi.where(), serverSelectionTimeoutMS=5000) db = client[db_name] collection = db["agent_memories"]
memory_doc = { "memory_text": memory_text, "agent_id": memory_agent_id, "user_id": user_id, "timestamp": datetime.utcnow(), "created_at": datetime.utcnow().isoformat() }
result = collection.insert_one(memory_doc) client.close()
return f"Memory stored with ID: {result.inserted_id}"
except Exception as e: return f"Error storing memory: {str(e)}"
def search_mongodb_memory(query: str, memory_agent_id: str, limit: int = 5) -> str: """ Search for memories in MongoDB using text search.
Args: query: The search query to find relevant memories memory_agent_id: The ID of the agent whose memories to search limit: Maximum number of results to return
Returns: Formatted string containing matching memories """ import pymongo import certifi
try: limit = int(limit) if limit else 5
mongodb_uri = os.getenv("MONGODB_URI") db_name = os.getenv("MONGODB_DB_NAME")
if not all([mongodb_uri, db_name]): return "Error: MongoDB credentials not configured"
client = pymongo.MongoClient(mongodb_uri, tlsCAFile=certifi.where(), serverSelectionTimeoutMS=5000) db = client[db_name] collection = db["agent_memories"]
# Search using text search results = collection.find( { "$and": [ {"agent_id": memory_agent_id}, {"$text": {"$search": query}} ] }, {"score": {"$meta": "textScore"}} ).sort([("score", {"$meta": "textScore"})]).limit(limit)
memories = [] for doc in results: memory_text = doc.get("memory_text", "") timestamp = doc.get("created_at", "Unknown time") memories.append(f"[{timestamp}] {memory_text}")
client.close()
# Fall back to recent memories if no text search results if not memories: client = pymongo.MongoClient(mongodb_uri, tlsCAFile=certifi.where(), serverSelectionTimeoutMS=5000) db = client[db_name] collection = db["agent_memories"]
results = collection.find( {"agent_id": memory_agent_id} ).sort("timestamp", pymongo.DESCENDING).limit(limit)
for doc in results: memory_text = doc.get("memory_text", "") timestamp = doc.get("created_at", "Unknown time") memories.append(f"[{timestamp}] {memory_text}")
client.close()
if not memories: return "No memories found"
return "\n\n".join(memories)
except Exception as e: return f"Error searching memories: {str(e)}"/** * MongoDB Memory Tools (Python code as string for Letta) * Letta tools execute in Python, so we define the Python source code here. */
export const insertMemoryToolCode = `import os
def insert_memory(memory_text: str, memory_agent_id: str, user_id: str = "default_user") -> str: """ Store a memory in MongoDB for a specific agent and user.
Args: memory_text: The memory content to store memory_agent_id: The ID of the agent storing this memory user_id: The ID of the user this memory relates to
Returns: Confirmation message with the inserted memory ID """ import pymongo import certifi from datetime import datetime
try: mongodb_uri = os.getenv("MONGODB_URI") db_name = os.getenv("MONGODB_DB_NAME")
if not all([mongodb_uri, db_name]): return "Error: MongoDB credentials not configured"
client = pymongo.MongoClient(mongodb_uri, tlsCAFile=certifi.where(), serverSelectionTimeoutMS=5000) db = client[db_name] collection = db["agent_memories"]
memory_doc = { "memory_text": memory_text, "agent_id": memory_agent_id, "user_id": user_id, "timestamp": datetime.utcnow(), "created_at": datetime.utcnow().isoformat() }
result = collection.insert_one(memory_doc) client.close()
return f"Memory stored with ID: {result.inserted_id}"
except Exception as e: return f"Error storing memory: {str(e)}"`;
export const searchMemoryToolCode = `import os
def search_mongodb_memory(query: str, memory_agent_id: str, limit: int = 5) -> str: """ Search for memories in MongoDB using text search.
Args: query: The search query to find relevant memories memory_agent_id: The ID of the agent whose memories to search limit: Maximum number of results to return
Returns: Formatted string containing matching memories """ import pymongo import certifi
try: limit = int(limit) if limit else 5
mongodb_uri = os.getenv("MONGODB_URI") db_name = os.getenv("MONGODB_DB_NAME")
if not all([mongodb_uri, db_name]): return "Error: MongoDB credentials not configured"
client = pymongo.MongoClient(mongodb_uri, tlsCAFile=certifi.where(), serverSelectionTimeoutMS=5000) db = client[db_name] collection = db["agent_memories"]
# Search using text search results = collection.find( { "$and": [ {"agent_id": memory_agent_id}, {"$text": {"$search": query}} ] }, {"score": {"$meta": "textScore"}} ).sort([("score", {"$meta": "textScore"})]).limit(limit)
memories = [] for doc in results: memory_text = doc.get("memory_text", "") timestamp = doc.get("created_at", "Unknown time") memories.append(f"[{timestamp}] {memory_text}")
client.close()
# Fall back to recent memories if no text search results if not memories: client = pymongo.MongoClient(mongodb_uri, tlsCAFile=certifi.where(), serverSelectionTimeoutMS=5000) db = client[db_name] collection = db["agent_memories"]
results = collection.find( {"agent_id": memory_agent_id} ).sort("timestamp", pymongo.DESCENDING).limit(limit)
for doc in results: memory_text = doc.get("memory_text", "") timestamp = doc.get("created_at", "Unknown time") memories.append(f"[{timestamp}] {memory_text}")
client.close()
if not memories: return "No memories found"
return "\\\\n\\\\n".join(memories)
except Exception as e: return f"Error searching memories: {str(e)}"`;The insert_memory function stores memories as documents in MongoDB with timestamps and metadata. The search_mongodb_memory function uses MongoDB’s text search index to find relevant memories, with a fallback to returning recent memories if no text matches are found.
import osfrom datetime import datetime, timezone
def insert_memory(memory_text: str, memory_agent_id: str, user_id: str = "default_user") -> str: """ Store a memory in Graphiti knowledge graph with temporal tracking.
Args: memory_text: The memory content to store memory_agent_id: The ID of the agent storing this memory user_id: The ID of the user this memory relates to
Returns: Confirmation message """ import asyncio from datetime import datetime, timezone from graphiti_core import Graphiti from graphiti_core.nodes import EpisodeType
async def add_memory(): try: neo4j_uri = os.getenv("NEO4J_URI") neo4j_user = os.getenv("NEO4J_USER") neo4j_password = os.getenv("NEO4J_PASSWORD")
if not all([neo4j_uri, neo4j_user, neo4j_password]): return "Error: Neo4j configuration not found"
graphiti = Graphiti(neo4j_uri, neo4j_user, neo4j_password)
await graphiti.add_episode( name=f"Memory for {memory_agent_id}", episode_body=f"[Agent: {memory_agent_id}] [User: {user_id}] {memory_text}", source=EpisodeType.text, source_description=f"agent_memory_{memory_agent_id}", reference_time=datetime.now(timezone.utc) )
await graphiti.close() return f"Memory stored in knowledge graph"
except Exception as e: return f"Error storing memory: {str(e)}"
try: loop = asyncio.get_running_loop() import concurrent.futures with concurrent.futures.ThreadPoolExecutor() as executor: future = executor.submit(asyncio.run, add_memory()) return future.result() except RuntimeError: return asyncio.run(add_memory())
def search_graphiti_memory(query: str, memory_agent_id: str, limit: int = 5) -> str: """ Search for memories using hybrid search (semantic + keyword + graph).
Args: query: The search query to find relevant memories memory_agent_id: The ID of the agent whose memories to search limit: Maximum number of results to return
Returns: Formatted string containing relevant memories """ import asyncio from graphiti_core import Graphiti
async def search_memories(): try: limit_int = int(limit) if limit else 5
neo4j_uri = os.getenv("NEO4J_URI") neo4j_user = os.getenv("NEO4J_USER") neo4j_password = os.getenv("NEO4J_PASSWORD")
if not all([neo4j_uri, neo4j_user, neo4j_password]): return "Error: Neo4j configuration not found"
graphiti = Graphiti(neo4j_uri, neo4j_user, neo4j_password)
search_query = f"[Agent: {memory_agent_id}] {query}" results = await graphiti.search(query=search_query, num_results=limit_int)
await graphiti.close()
if not results: return "No memories found"
memories = [] for edge in results[:limit_int]: if hasattr(edge, 'fact') and edge.fact: fact_text = edge.fact if f"[Agent: {memory_agent_id}]" in fact_text: fact_text = fact_text.split(f"[Agent: {memory_agent_id}]")[-1].strip() if fact_text: memories.append(fact_text)
if not memories: return "No relevant memories found"
return "\n\n".join(memories)
except Exception as e: return f"Error searching memories: {str(e)}"
try: loop = asyncio.get_running_loop() import concurrent.futures with concurrent.futures.ThreadPoolExecutor() as executor: future = executor.submit(asyncio.run, search_memories()) return future.result() except RuntimeError: return asyncio.run(search_memories())/** * Graphiti Memory Tools (Python code as string for Letta) * Letta tools execute in Python, so we define the Python source code here. */
export const insertMemoryToolCode = `import osfrom datetime import datetime, timezone
def insert_memory(memory_text: str, memory_agent_id: str, user_id: str = "default_user") -> str: """ Store a memory in Graphiti knowledge graph with temporal tracking.
Args: memory_text: The memory content to store memory_agent_id: The ID of the agent storing this memory user_id: The ID of the user this memory relates to
Returns: Confirmation message """ import asyncio from datetime import datetime, timezone from graphiti_core import Graphiti from graphiti_core.nodes import EpisodeType
async def add_memory(): try: neo4j_uri = os.getenv("NEO4J_URI") neo4j_user = os.getenv("NEO4J_USER") neo4j_password = os.getenv("NEO4J_PASSWORD")
if not all([neo4j_uri, neo4j_user, neo4j_password]): return "Error: Neo4j configuration not found"
graphiti = Graphiti(neo4j_uri, neo4j_user, neo4j_password)
await graphiti.add_episode( name=f"Memory for {memory_agent_id}", episode_body=f"[Agent: {memory_agent_id}] [User: {user_id}] {memory_text}", source=EpisodeType.text, source_description=f"agent_memory_{memory_agent_id}", reference_time=datetime.now(timezone.utc) )
await graphiti.close() return f"Memory stored in knowledge graph"
except Exception as e: return f"Error storing memory: {str(e)}"
try: loop = asyncio.get_running_loop() import concurrent.futures with concurrent.futures.ThreadPoolExecutor() as executor: future = executor.submit(asyncio.run, add_memory()) return future.result() except RuntimeError: return asyncio.run(add_memory())`;
export const searchMemoryToolCode = `import os
def search_graphiti_memory(query: str, memory_agent_id: str, limit: int = 5) -> str: """ Search for memories using hybrid search (semantic + keyword + graph).
Args: query: The search query to find relevant memories memory_agent_id: The ID of the agent whose memories to search limit: Maximum number of results to return
Returns: Formatted string containing relevant memories """ import asyncio from graphiti_core import Graphiti
async def search_memories(): try: limit_int = int(limit) if limit else 5
neo4j_uri = os.getenv("NEO4J_URI") neo4j_user = os.getenv("NEO4J_USER") neo4j_password = os.getenv("NEO4J_PASSWORD")
if not all([neo4j_uri, neo4j_user, neo4j_password]): return "Error: Neo4j configuration not found"
graphiti = Graphiti(neo4j_uri, neo4j_user, neo4j_password)
search_query = f"[Agent: {memory_agent_id}] {query}" results = await graphiti.search(query=search_query, num_results=limit_int)
await graphiti.close()
if not results: return "No memories found"
memories = [] for edge in results[:limit_int]: if hasattr(edge, 'fact') and edge.fact: fact_text = edge.fact if f"[Agent: {memory_agent_id}]" in fact_text: fact_text = fact_text.split(f"[Agent: {memory_agent_id}]")[-1].strip() if fact_text: memories.append(fact_text)
if not memories: return "No relevant memories found"
return "\\\\n\\\\n".join(memories)
except Exception as e: return f"Error searching memories: {str(e)}"
try: loop = asyncio.get_running_loop() import concurrent.futures with concurrent.futures.ThreadPoolExecutor() as executor: future = executor.submit(asyncio.run, search_memories()) return future.result() except RuntimeError: return asyncio.run(search_memories())`;Memories are stored as episodes in a temporal knowledge graph with automatic entity and relationship extraction. The search_graphiti_memory function uses hybrid search combining semantic similarity, keyword matching, and graph traversal to find connected information across time.
import os
def insert_memory(memory_text: str, memory_agent_id: str, user_id: str = "default_user") -> str: """ Store a memory in Weaviate with automatic vectorization.
Args: memory_text: The memory content to store memory_agent_id: The ID of the agent storing this memory user_id: The ID of the user this memory relates to
Returns: Confirmation message with the inserted memory UUID """ import weaviate from weaviate.classes.init import Auth from datetime import datetime
try: weaviate_url = os.getenv("WEAVIATE_URL") weaviate_api_key = os.getenv("WEAVIATE_API_KEY") openai_api_key = os.getenv("OPENAI_API_KEY")
if not all([weaviate_url, weaviate_api_key, openai_api_key]): return "Error: Weaviate credentials not configured"
client = weaviate.connect_to_weaviate_cloud( cluster_url=weaviate_url, auth_credentials=Auth.api_key(weaviate_api_key), headers={"X-OpenAI-Api-Key": openai_api_key} )
collection = client.collections.get("AgentMemory")
memory_obj = { "memory_text": memory_text, "agent_id": memory_agent_id, "user_id": user_id, "created_at": datetime.utcnow().isoformat() }
uuid = collection.data.insert(memory_obj) client.close()
return f"Memory stored with ID: {uuid}"
except Exception as e: return f"Error storing memory: {str(e)}"
def search_weaviate_memory(query: str, memory_agent_id: str, limit: int = 5) -> str: """ Search for memories using vector similarity search.
Args: query: The search query to find relevant memories memory_agent_id: The ID of the agent whose memories to search limit: Maximum number of results to return
Returns: Formatted string containing similar memories """ import weaviate from weaviate.classes.init import Auth from weaviate.classes.query import Filter
try: limit = int(limit) if limit else 5
weaviate_url = os.getenv("WEAVIATE_URL") weaviate_api_key = os.getenv("WEAVIATE_API_KEY") openai_api_key = os.getenv("OPENAI_API_KEY")
if not all([weaviate_url, weaviate_api_key, openai_api_key]): return "Error: Weaviate credentials not configured"
client = weaviate.connect_to_weaviate_cloud( cluster_url=weaviate_url, auth_credentials=Auth.api_key(weaviate_api_key), headers={"X-OpenAI-Api-Key": openai_api_key} )
collection = client.collections.get("AgentMemory")
response = collection.query.near_text( query=query, filters=Filter.by_property("agent_id").equal(memory_agent_id), limit=limit, return_properties=["memory_text", "created_at", "user_id"] )
memories = [] for obj in response.objects: memory_text = obj.properties.get("memory_text", "") timestamp = obj.properties.get("created_at", "Unknown time") memories.append(f"[{timestamp}] {memory_text}")
client.close()
if not memories: return "No memories found"
return "\n\n".join(memories)
except Exception as e: return f"Error searching memories: {str(e)}"/** * Weaviate Memory Tools (Python code as string for Letta) * Letta tools execute in Python, so we define the Python source code here. */
export const insertMemoryToolCode = `import os
def insert_memory(memory_text: str, memory_agent_id: str, user_id: str = "default_user") -> str: """ Store a memory in Weaviate with automatic vectorization.
Args: memory_text: The memory content to store memory_agent_id: The ID of the agent storing this memory user_id: The ID of the user this memory relates to
Returns: Confirmation message with the inserted memory UUID """ import weaviate from weaviate.classes.init import Auth from datetime import datetime
try: weaviate_url = os.getenv("WEAVIATE_URL") weaviate_api_key = os.getenv("WEAVIATE_API_KEY") openai_api_key = os.getenv("OPENAI_API_KEY")
if not all([weaviate_url, weaviate_api_key, openai_api_key]): return "Error: Weaviate credentials not configured"
client = weaviate.connect_to_weaviate_cloud( cluster_url=weaviate_url, auth_credentials=Auth.api_key(weaviate_api_key), headers={"X-OpenAI-Api-Key": openai_api_key} )
collection = client.collections.get("AgentMemory")
memory_obj = { "memory_text": memory_text, "agent_id": memory_agent_id, "user_id": user_id, "created_at": datetime.utcnow().isoformat() }
uuid = collection.data.insert(memory_obj) client.close()
return f"Memory stored with ID: {uuid}"
except Exception as e: return f"Error storing memory: {str(e)}"`;
export const searchMemoryToolCode = `import os
def search_weaviate_memory(query: str, memory_agent_id: str, limit: int = 5) -> str: """ Search for memories using vector similarity search.
Args: query: The search query to find relevant memories memory_agent_id: The ID of the agent whose memories to search limit: Maximum number of results to return
Returns: Formatted string containing similar memories """ import weaviate from weaviate.classes.init import Auth from weaviate.classes.query import Filter
try: limit = int(limit) if limit else 5
weaviate_url = os.getenv("WEAVIATE_URL") weaviate_api_key = os.getenv("WEAVIATE_API_KEY") openai_api_key = os.getenv("OPENAI_API_KEY")
if not all([weaviate_url, weaviate_api_key, openai_api_key]): return "Error: Weaviate credentials not configured"
client = weaviate.connect_to_weaviate_cloud( cluster_url=weaviate_url, auth_credentials=Auth.api_key(weaviate_api_key), headers={"X-OpenAI-Api-Key": openai_api_key} )
collection = client.collections.get("AgentMemory")
response = collection.query.near_text( query=query, filters=Filter.by_property("agent_id").equal(memory_agent_id), limit=limit, return_properties=["memory_text", "created_at", "user_id"] )
memories = [] for obj in response.objects: memory_text = obj.properties.get("memory_text", "") timestamp = obj.properties.get("created_at", "Unknown time") memories.append(f"[{timestamp}] {memory_text}")
client.close()
if not memories: return "No memories found"
return "\\\\n\\\\n".join(memories)
except Exception as e: return f"Error searching memories: {str(e)}"`;Memories are automatically vectorized using OpenAI embeddings when stored. The search_weaviate_memory function performs a vector similarity search to find semantically related memories, even if they don’t share exact keywords.
import osimport jsonfrom typing import Optional
def insert_memory( content: str, memory_agent_id: str, user_id: str, metadata: Optional[str] = None) -> str: """ Store a memory in Mem0 with automatic extraction and organization.
Args: content: The memory content to store memory_agent_id: The ID of the agent storing this memory user_id: The ID of the user this memory relates to metadata: Optional JSON string with additional metadata
Returns: JSON string with success status and result """ from mem0 import MemoryClient
try: api_key = os.getenv("MEM0_API_KEY") if not api_key: return json.dumps({"success": False, "error": "MEM0_API_KEY not set"})
client = MemoryClient(api_key=api_key)
extra_metadata = {} if metadata: try: extra_metadata = json.loads(metadata) except json.JSONDecodeError: return json.dumps({"success": False, "error": "Invalid JSON in metadata"})
result = client.add( messages=content, agent_id=memory_agent_id, user_id=user_id, metadata=extra_metadata if extra_metadata else None, version="v2" )
return json.dumps({ "success": True, "message": "Memory stored", "result": result })
except Exception as e: return json.dumps({"success": False, "error": str(e)})
def search_mem0_memory( query: str, memory_agent_id: str, user_id: str, limit: int = 5) -> str: """ Search for memories using semantic search.
Args: query: The search query to find relevant memories memory_agent_id: The ID of the agent whose memories to search user_id: The ID of the user whose memories to search limit: Maximum number of results to return
Returns: JSON string with memories and metadata """ from mem0 import MemoryClient
try: api_key = os.getenv("MEM0_API_KEY") if not api_key: return json.dumps({"success": False, "error": "MEM0_API_KEY not set"})
client = MemoryClient(api_key=api_key)
results = client.search( query=query, filters={ "OR": [ {"user_id": user_id}, {"agent_id": memory_agent_id} ] }, limit=limit, version="v2" )
memories = [] if isinstance(results, dict) and "results" in results: memories = results["results"] elif isinstance(results, list): memories = results
return json.dumps({ "success": True, "count": len(memories), "memories": memories }, indent=2)
except Exception as e: return json.dumps({"success": False, "error": str(e)})/** * Mem0 Memory Tools (Python code as string for Letta) * Letta tools execute in Python, so we define the Python source code here. */
export const insertMemoryToolCode = `import osimport jsonfrom typing import Optional
def insert_memory( content: str, memory_agent_id: str, user_id: str, metadata: Optional[str] = None) -> str: """ Store a memory in Mem0 with automatic extraction and organization.
Args: content: The memory content to store memory_agent_id: The ID of the agent storing this memory user_id: The ID of the user this memory relates to metadata: Optional JSON string with additional metadata
Returns: JSON string with success status and result """ from mem0 import MemoryClient
try: api_key = os.getenv("MEM0_API_KEY") if not api_key: return json.dumps({"success": False, "error": "MEM0_API_KEY not set"})
client = MemoryClient(api_key=api_key)
extra_metadata = {} if metadata: try: extra_metadata = json.loads(metadata) except json.JSONDecodeError: return json.dumps({"success": False, "error": "Invalid JSON in metadata"})
result = client.add( messages=content, agent_id=memory_agent_id, user_id=user_id, metadata=extra_metadata if extra_metadata else None, version="v2" )
return json.dumps({ "success": True, "message": "Memory stored", "result": result })
except Exception as e: return json.dumps({"success": False, "error": str(e)})`;
export const searchMemoryToolCode = `import osimport json
def search_mem0_memory( query: str, memory_agent_id: str, user_id: str, limit: int = 5) -> str: """ Search for memories using semantic search.
Args: query: The search query to find relevant memories memory_agent_id: The ID of the agent whose memories to search user_id: The ID of the user whose memories to search limit: Maximum number of results to return
Returns: JSON string with memories and metadata """ from mem0 import MemoryClient
try: api_key = os.getenv("MEM0_API_KEY") if not api_key: return json.dumps({"success": False, "error": "MEM0_API_KEY not set"})
client = MemoryClient(api_key=api_key)
results = client.search( query=query, filters={ "OR": [ {"user_id": user_id}, {"agent_id": memory_agent_id} ] }, limit=limit, version="v2" )
memories = [] if isinstance(results, dict) and "results" in results: memories = results["results"] elif isinstance(results, list): memories = results
return json.dumps({ "success": True, "count": len(memories), "memories": memories }, indent=2)
except Exception as e: return json.dumps({"success": False, "error": str(e)})`;Mem0 is a fully managed service that automatically handles intelligent memory extraction and organization. The insert_memory function sends content to Mem0’s API, which extracts entities and facts. The search_mem0_memory function uses semantic search to retrieve relevant memories with metadata.
import os
def insert_memory(memory_text: str, memory_agent_id: str, user_id: str = "default_user") -> str: """ Store a memory in Zep thread-based storage.
Args: memory_text: The memory content to store memory_agent_id: The ID of the agent storing this memory user_id: The ID of the user this memory relates to
Returns: Confirmation message """ from zep_cloud.client import Zep from zep_cloud import Message
try: api_key = os.environ.get("ZEP_API_KEY") if not api_key: return "Error: ZEP_API_KEY not set"
client = Zep(api_key=api_key) thread_id = f"{memory_agent_id}_{user_id}"
# Ensure user exists try: client.user.get(user_id=user_id) except: client.user.add(user_id=user_id)
# Ensure thread exists try: client.thread.get(thread_id=thread_id) except: client.thread.create(thread_id=thread_id, user_id=user_id)
# Add message to thread message = Message(role="user", content=memory_text) client.thread.add_messages(thread_id=thread_id, messages=[message])
return f"Memory stored in thread {thread_id}"
except Exception as e: return f"Error storing memory: {str(e)}"
def search_zep_memory(query: str, memory_agent_id: str, user_id: str = "user", limit: int = 5) -> str: """ Search for memories using semantic search with knowledge graph.
Args: query: The search query to find relevant memories memory_agent_id: The ID of the agent whose memories to search user_id: The ID of the user whose memories to search limit: Maximum number of results to return
Returns: Formatted string containing relevant context from memory """ from zep_cloud.client import Zep
try: api_key = os.environ.get("ZEP_API_KEY") if not api_key: return "Error: ZEP_API_KEY not set"
client = Zep(api_key=api_key) thread_id = f"{memory_agent_id}_{user_id}"
response = client.thread.get_user_context(thread_id=thread_id)
if not response or not response.context: return "No memories found"
return f"Relevant memories:\n\n{response.context}"
except Exception as e: if "not found" in str(e).lower() or "does not exist" in str(e).lower(): return "No memories found" return f"Error searching memories: {str(e)}"/** * Zep Memory Tools (Python code as string for Letta) * Letta tools execute in Python, so we define the Python source code here. */
export const insertMemoryToolCode = `import os
def insert_memory(memory_text: str, memory_agent_id: str, user_id: str = "default_user") -> str: """ Store a memory in Zep thread-based storage.
Args: memory_text: The memory content to store memory_agent_id: The ID of the agent storing this memory user_id: The ID of the user this memory relates to
Returns: Confirmation message """ from zep_cloud.client import Zep from zep_cloud import Message
try: api_key = os.environ.get("ZEP_API_KEY") if not api_key: return "Error: ZEP_API_KEY not set"
client = Zep(api_key=api_key) thread_id = f"{memory_agent_id}_{user_id}"
# Ensure user exists try: client.user.get(user_id=user_id) except: client.user.add(user_id=user_id)
# Ensure thread exists try: client.thread.get(thread_id=thread_id) except: client.thread.create(thread_id=thread_id, user_id=user_id)
# Add message to thread message = Message(role="user", content=memory_text) client.thread.add_messages(thread_id=thread_id, messages=[message])
return f"Memory stored in thread {thread_id}"
except Exception as e: return f"Error storing memory: {str(e)}"`;
export const searchMemoryToolCode = `import os
def search_zep_memory(query: str, memory_agent_id: str, user_id: str = "user", limit: int = 5) -> str: """ Search for memories using semantic search with knowledge graph.
Args: query: The search query to find relevant memories memory_agent_id: The ID of the agent whose memories to search user_id: The ID of the user whose memories to search limit: Maximum number of results to return
Returns: Formatted string containing relevant context from memory """ from zep_cloud.client import Zep
try: api_key = os.environ.get("ZEP_API_KEY") if not api_key: return "Error: ZEP_API_KEY not set"
client = Zep(api_key=api_key) thread_id = f"{memory_agent_id}_{user_id}"
response = client.thread.get_user_context(thread_id=thread_id)
if not response or not response.context: return "No memories found"
return f"Relevant memories:\\\\n\\\\n{response.context}"
except Exception as e: if "not found" in str(e).lower() or "does not exist" in str(e).lower(): return "No memories found" return f"Error searching memories: {str(e)}"`;Zep organizes memories in session-based threads with automatic summarization and knowledge graph technology. The insert_memory function stores memories in user-specific threads, while search_zep_memory retrieves context-aware information, including facts, entities, and episodes from the conversation history.
Now we’ll create an agent and attach our custom memory tools to it. You need to do the following:
The agent’s persona guides its behavior, instructing it to proactively store important information and retrieve relevant context when needed.
Create a file named create_agent.py or create_agent.ts:
import osfrom letta_client import Lettafrom dotenv import load_dotenvfrom tools import insert_memory, search_mongodb_memory
load_dotenv()
def main(): letta_api_key = os.getenv("LETTA_API_KEY") if not letta_api_key: print("Error: LETTA_API_KEY not found") return
client = Letta(api_key=letta_api_key)
print("Creating memory tools...")
insert_tool = client.tools.create_from_function( func=insert_memory, pip_requirements=[ {"name": "pymongo"}, {"name": "certifi"}, {"name": "dnspython"} ] ) print(f"Created tool: {insert_tool.name}")
search_tool = client.tools.create_from_function( func=search_mongodb_memory, pip_requirements=[ {"name": "pymongo"}, {"name": "certifi"}, {"name": "dnspython"} ] ) print(f"Created tool: {search_tool.name}")
persona = """You are a helpful assistant with persistent memory.- Store important information using insert_memory- Retrieve past information using search_mongodb_memory- Be proactive about remembering user preferences and details"""
print("Creating agent...")
agent = client.agents.create( name="MongoDB Memory Assistant", description="An assistant that stores memories in MongoDB", model="openai/gpt-4o-mini", embedding="openai/text-embedding-3-small", memory_blocks=[{"label": "persona", "value": persona}], tools=[insert_tool.name, search_tool.name], include_base_tools=False, secrets={ "MONGODB_URI": os.getenv("MONGODB_URI"), "MONGODB_DB_NAME": os.getenv("MONGODB_DB_NAME") } )
print(f"\nAgent created: {agent.name}") print(f"Agent ID: {agent.id}") print(f"\nUse this agent ID in chat.py")
if __name__ == "__main__": main()import Letta from '@letta-ai/letta-client';import * as dotenv from 'dotenv';import { insertMemoryToolCode, searchMemoryToolCode } from './tools.js';
dotenv.config();
async function main() { const lettaApiKey = process.env.LETTA_API_KEY; if (!lettaApiKey) { console.error('Error: LETTA_API_KEY not found'); return; }
const client = new Letta({ apiKey: lettaApiKey });
console.log('Creating memory tools...');
// Create insert_memory tool const insertTool = await client.tools.create({ source_code: insertMemoryToolCode, source_type: 'python', pip_requirements: [ { name: 'pymongo' }, { name: 'certifi' }, { name: 'dnspython' } ] }); console.log(`Created tool: ${insertTool.name}`);
// Create search_mongodb_memory tool const searchTool = await client.tools.create({ source_code: searchMemoryToolCode, source_type: 'python', pip_requirements: [ { name: 'pymongo' }, { name: 'certifi' }, { name: 'dnspython' } ] }); console.log(`Created tool: ${searchTool.name}`);
const persona = `You are a helpful assistant with persistent memory.- Store important information using insert_memory- Retrieve past information using search_mongodb_memory- Be proactive about remembering user preferences and details`;
console.log('Creating agent...');
const agent = await client.agents.create({ name: 'MongoDB Memory Assistant', description: 'An assistant that stores memories in MongoDB', memory_blocks: [ { label: 'persona', value: persona } ], tool_ids: [insertTool.id, searchTool.id], include_base_tools: false, secrets: { MONGODB_URI: process.env.MONGODB_URI || '', MONGODB_DB_NAME: process.env.MONGODB_DB_NAME || '' } });
console.log(`\nAgent created: ${agent.name}`); console.log(`Agent ID: ${agent.id}`); console.log(`\nUse this agent ID in chat.ts`);}
main().catch(console.error);import osfrom letta_client import Lettafrom dotenv import load_dotenvfrom tools import insert_memory, search_graphiti_memory
load_dotenv()
def main(): letta_api_key = os.getenv("LETTA_API_KEY") if not letta_api_key: print("Error: LETTA_API_KEY not found") return
client = Letta(api_key=letta_api_key)
print("Creating Graphiti memory tools...")
insert_tool = client.tools.create_from_function( func=insert_memory, pip_requirements=[{"name": "graphiti-core"}] ) print(f"Created tool: {insert_tool.name}")
search_tool = client.tools.create_from_function( func=search_graphiti_memory, pip_requirements=[{"name": "graphiti-core"}] ) print(f"Created tool: {search_tool.name}")
persona = """You are a helpful assistant with temporal knowledge graph memory.- Store important information using insert_memory- Retrieve past information using search_graphiti_memory- The knowledge graph tracks relationships and temporal connections"""
print("Creating agent...")
agent = client.agents.create( name="Graphiti Memory Assistant", description="An assistant that stores memories in a temporal knowledge graph", model="openai/gpt-4o-mini", embedding="openai/text-embedding-3-small", memory_blocks=[{"label": "persona", "value": persona}], tools=[insert_tool.name, search_tool.name], include_base_tools=False, secrets={ "OPENAI_API_KEY": os.getenv("OPENAI_API_KEY"), "NEO4J_URI": os.getenv("NEO4J_URI"), "NEO4J_USER": os.getenv("NEO4J_USER"), "NEO4J_PASSWORD": os.getenv("NEO4J_PASSWORD") } )
print(f"\nAgent created: {agent.name}") print(f"Agent ID: {agent.id}") print(f"\nUse this agent ID in chat.py")
if __name__ == "__main__": main()import Letta from '@letta-ai/letta-client';import * as dotenv from 'dotenv';import { insertMemoryToolCode, searchMemoryToolCode } from './tools.js';
dotenv.config();
async function main() { const lettaApiKey = process.env.LETTA_API_KEY; if (!lettaApiKey) { console.error('Error: LETTA_API_KEY not found'); return; }
const client = new Letta({ apiKey: lettaApiKey });
console.log('Creating Graphiti memory tools...');
// Create insert_memory tool const insertTool = await client.tools.create({ source_code: insertMemoryToolCode, source_type: 'python', pip_requirements: [ { name: 'graphiti-core' } ] }); console.log(`Created tool: ${insertTool.name}`);
// Create search_graphiti_memory tool const searchTool = await client.tools.create({ source_code: searchMemoryToolCode, source_type: 'python', pip_requirements: [ { name: 'graphiti-core' } ] }); console.log(`Created tool: ${searchTool.name}`);
const persona = `You are a helpful assistant with temporal knowledge graph memory.- Store important information using insert_memory- Retrieve past information using search_graphiti_memory- The knowledge graph tracks relationships and temporal connections`;
console.log('Creating agent...');
const agent = await client.agents.create({ name: 'Graphiti Memory Assistant', description: 'An assistant that stores memories in a temporal knowledge graph', memory_blocks: [ { label: 'persona', value: persona } ], tool_ids: [insertTool.id, searchTool.id], include_base_tools: false, secrets: { OPENAI_API_KEY: process.env.OPENAI_API_KEY || '', NEO4J_URI: process.env.NEO4J_URI || '', NEO4J_USER: process.env.NEO4J_USER || '', NEO4J_PASSWORD: process.env.NEO4J_PASSWORD || '' } });
console.log(`\nAgent created: ${agent.name}`); console.log(`Agent ID: ${agent.id}`); console.log(`\nUse this agent ID in chat.ts`);}
main().catch(console.error);import osfrom letta_client import Lettafrom dotenv import load_dotenvfrom tools import insert_memory, search_weaviate_memory
load_dotenv()
def main(): letta_api_key = os.getenv("LETTA_API_KEY") if not letta_api_key: print("Error: LETTA_API_KEY not found") return
client = Letta(api_key=letta_api_key)
print("Creating Weaviate memory tools...")
insert_tool = client.tools.create_from_function( func=insert_memory, pip_requirements=[{"name": "weaviate-client"}] ) print(f"Created tool: {insert_tool.name}")
search_tool = client.tools.create_from_function( func=search_weaviate_memory, pip_requirements=[{"name": "weaviate-client"}] ) print(f"Created tool: {search_tool.name}")
persona = """You are a helpful assistant with vector search memory.- Store important information using insert_memory- Retrieve past information using search_weaviate_memory- Use semantic search to find related memories"""
print("Creating agent...")
agent = client.agents.create( name="Weaviate Memory Assistant", description="An assistant that stores memories in Weaviate using vector search", model="openai/gpt-4o-mini", embedding="openai/text-embedding-3-small", memory_blocks=[{"label": "persona", "value": persona}], tools=[insert_tool.name, search_tool.name], include_base_tools=False, secrets={ "WEAVIATE_URL": os.getenv("WEAVIATE_URL"), "WEAVIATE_API_KEY": os.getenv("WEAVIATE_API_KEY"), "OPENAI_API_KEY": os.getenv("OPENAI_API_KEY") } )
print(f"\nAgent created: {agent.name}") print(f"Agent ID: {agent.id}") print(f"\nUse this agent ID in chat.py")
if __name__ == "__main__": main()import Letta from '@letta-ai/letta-client';import * dotenv from 'dotenv';import { insertMemoryToolCode, searchMemoryToolCode } from './tools.js';
dotenv.config();
async function main() { const lettaApiKey = process.env.LETTA_API_KEY; if (!lettaApiKey) { console.error('Error: LETTA_API_KEY not found'); return; }
const client = new Letta({ apiKey: lettaApiKey });
console.log('Creating Weaviate memory tools...');
// Create insert_memory tool const insertTool = await client.tools.create({ source_code: insertMemoryToolCode, source_type: 'python', pip_requirements: [ { name: 'weaviate-client' } ] }); console.log(`Created tool: ${insertTool.name}`);
// Create search_weaviate_memory tool const searchTool = await client.tools.create({ source_code: searchMemoryToolCode, source_type: 'python', pip_requirements: [ { name: 'weaviate-client' } ] }); console.log(`Created tool: ${searchTool.name}`);
const persona = `You are a helpful assistant with vector search memory.- Store important information using insert_memory- Retrieve past information using search_weaviate_memory- Use semantic search to find related memories`;
console.log('Creating agent...');
const agent = await client.agents.create({ name: 'Weaviate Memory Assistant', description: 'An assistant that stores memories in Weaviate using vector search', memory_blocks: [ { label: 'persona', value: persona } ], tool_ids: [insertTool.id, searchTool.id], include_base_tools: false, secrets: { WEAVIATE_URL: process.env.WEAVIATE_URL || '', WEAVIATE_API_KEY: process.env.WEAVIATE_API_KEY || '', OPENAI_API_KEY: process.env.OPENAI_API_KEY || '' } });
console.log(`\nAgent created: ${agent.name}`); console.log(`Agent ID: ${agent.id}`); console.log(`\nUse this agent ID in chat.ts`);}
main().catch(console.error);import osfrom dotenv import load_dotenvfrom letta_client import Lettafrom tools import insert_memory, search_mem0_memory
load_dotenv()
def main(): letta_api_key = os.getenv("LETTA_API_KEY") if not letta_api_key: print("Error: LETTA_API_KEY not found") return
client = Letta(api_key=letta_api_key)
print("Creating Mem0 memory tools...")
insert_tool = client.tools.create_from_function( func=insert_memory, pip_requirements=[{"name": "mem0ai"}] ) print(f"Created tool: {insert_tool.name}")
search_tool = client.tools.create_from_function( func=search_mem0_memory, pip_requirements=[{"name": "mem0ai"}] ) print(f"Created tool: {search_tool.name}")
persona = """You are a helpful assistant with Mem0 intelligent memory.- Store important information using insert_memory- Retrieve past information using search_mem0_memory- Mem0 automatically extracts and organizes information"""
print("Creating agent...")
agent = client.agents.create( name="Mem0 Memory Assistant", description="An assistant that stores memories in Mem0", model="openai/gpt-4o-mini", embedding="openai/text-embedding-3-small", memory_blocks=[{"label": "persona", "value": persona}], tools=[insert_tool.name, search_tool.name], include_base_tools=False, secrets={ "MEM0_API_KEY": os.getenv("MEM0_API_KEY") } )
print(f"\nAgent created: {agent.name}") print(f"Agent ID: {agent.id}") print(f"\nUse this agent ID in chat.py")
if __name__ == "__main__": main()import Letta from '@letta-ai/letta-client';import * as dotenv from 'dotenv';import { insertMemoryToolCode, searchMemoryToolCode } from './tools.js';
dotenv.config();
async function main() { const lettaApiKey = process.env.LETTA_API_KEY; if (!lettaApiKey) { console.error('Error: LETTA_API_KEY not found'); return; }
const client = new Letta({ apiKey: lettaApiKey });
console.log('Creating Mem0 memory tools...');
// Create insert_memory tool const insertTool = await client.tools.create({ source_code: insertMemoryToolCode, source_type: 'python', pip_requirements: [ { name: 'mem0ai' } ] }); console.log(`Created tool: ${insertTool.name}`);
// Create search_mem0_memory tool const searchTool = await client.tools.create({ source_code: searchMemoryToolCode, source_type: 'python', pip_requirements: [ { name: 'mem0ai' } ] }); console.log(`Created tool: ${searchTool.name}`);
const persona = `You are a helpful assistant with Mem0 intelligent memory.- Store important information using insert_memory- Retrieve past information using search_mem0_memory- Mem0 automatically extracts and organizes information`;
console.log('Creating agent...');
const agent = await client.agents.create({ name: 'Mem0 Memory Assistant', description: 'An assistant that stores memories in Mem0', memory_blocks: [ { label: 'persona', value: persona } ], tool_ids: [insertTool.id, searchTool.id], include_base_tools: false, secrets: { MEM0_API_KEY: process.env.MEM0_API_KEY || '' } });
console.log(`\nAgent created: ${agent.name}`); console.log(`Agent ID: ${agent.id}`); console.log(`\nUse this agent ID in chat.ts`);}
main().catch(console.error);import osfrom letta_client import Lettafrom dotenv import load_dotenvfrom tools import insert_memory, search_zep_memory
load_dotenv()
def main(): letta_api_key = os.getenv("LETTA_API_KEY") if not letta_api_key: print("Error: LETTA_API_KEY not found") return
client = Letta(api_key=letta_api_key)
print("Creating Zep memory tools...")
insert_tool = client.tools.create_from_function( func=insert_memory, pip_requirements=[{"name": "zep-cloud"}] ) print(f"Created tool: {insert_tool.name}")
search_tool = client.tools.create_from_function( func=search_zep_memory, pip_requirements=[{"name": "zep-cloud"}] ) print(f"Created tool: {search_tool.name}")
persona = """You are a helpful assistant with Zep knowledge graph memory.- Store important information using insert_memory- Retrieve past information using search_zep_memory- Zep uses knowledge graphs for context-aware retrieval"""
print("Creating agent...")
agent = client.agents.create( name="Zep Memory Assistant", description="An assistant that stores memories in Zep using knowledge graphs", model="openai/gpt-4o-mini", embedding="openai/text-embedding-3-small", memory_blocks=[{"label": "persona", "value": persona}], tools=[insert_tool.name, search_tool.name], include_base_tools=False, secrets={ "ZEP_API_KEY": os.getenv("ZEP_API_KEY") } )
print(f"\nAgent created: {agent.name}") print(f"Agent ID: {agent.id}") print(f"\nUse this agent ID in chat.py")
if __name__ == "__main__": main()import Letta from '@letta-ai/letta-client';import * as dotenv from 'dotenv';import { insertMemoryToolCode, searchMemoryToolCode } from './tools.js';
dotenv.config();
async function main() { const lettaApiKey = process.env.LETTA_API_KEY; if (!lettaApiKey) { console.error('Error: LETTA_API_KEY not found'); return; }
const client = new Letta({ apiKey: lettaApiKey });
console.log('Creating Zep memory tools...');
// Create insert_memory tool const insertTool = await client.tools.create({ source_code: insertMemoryToolCode, source_type: 'python', pip_requirements: [ { name: 'zep-cloud' } ] }); console.log(`Created tool: ${insertTool.name}`);
// Create search_zep_memory tool const searchTool = await client.tools.create({ source_code: searchMemoryToolCode, source_type: 'python', pip_requirements: [ { name: 'zep-cloud' } ] }); console.log(`Created tool: ${searchTool.name}`);
const persona = `You are a helpful assistant with Zep knowledge graph memory.- Store important information using insert_memory- Retrieve past information using search_zep_memory- Zep uses knowledge graphs for context-aware retrieval`;
console.log('Creating agent...');
const agent = await client.agents.create({ name: 'Zep Memory Assistant', description: 'An assistant that stores memories in Zep using knowledge graphs', memory_blocks: [ { label: 'persona', value: persona } ], tool_ids: [insertTool.id, searchTool.id], include_base_tools: false, secrets: { ZEP_API_KEY: process.env.ZEP_API_KEY || '' } });
console.log(`\nAgent created: ${agent.name}`); console.log(`Agent ID: ${agent.id}`); console.log(`\nUse this agent ID in chat.ts`);}
main().catch(console.error);Run this script once to create the agent:
python create_agent.pynpx tsx create_agent.tsYou have now fully configured your agent with custom memory tools and environment variables.
Now we’ll interact with the agent to test memory storage and retrieval.
Create a file named chat.py:
import osfrom letta_client import Lettafrom dotenv import load_dotenv
load_dotenv()
def main(): letta_api_key = os.getenv("LETTA_API_KEY") if not letta_api_key: print("Error: LETTA_API_KEY not found") return
letta_client = Letta(api_key=letta_api_key)
AGENT_ID = input("Enter your agent ID: ").strip() if not AGENT_ID: print("Error: Agent ID required") return
print("\nMongoDB Memory Assistant") print("Type 'exit' to quit\n")
while True: user_input = input("You: ").strip()
if user_input.lower() in ['exit', 'quit']: break
if not user_input: continue
try: response = letta_client.agents.messages.create( agent_id=AGENT_ID, messages=[{"role": "user", "content": user_input}] )
for message in response.messages: if message.message_type == 'assistant_message': print(f"\nAssistant: {message.content}\n")
except Exception as e: print(f"Error: {str(e)}\n")
if __name__ == "__main__": main()import Letta from '@letta-ai/letta-client';import * as dotenv from 'dotenv';import * as readline from 'readline';
dotenv.config();
async function main() { const lettaApiKey = process.env.LETTA_API_KEY; if (!lettaApiKey) { console.error('Error: LETTA_API_KEY not found'); return; }
const rl = readline.createInterface({ input: process.stdin, output: process.stdout });
const askQuestion = (query: string): Promise<string> => { return new Promise((resolve) => { rl.question(query, resolve); }); };
const agentId = (await askQuestion('Enter your agent ID: ')).trim(); if (!agentId) { console.error('Error: Agent ID required'); rl.close(); return; }
const client = new Letta({ apiKey: lettaApiKey });
console.log('\nMongoDB Memory Assistant'); console.log("Type 'exit' to quit\n");
while (true) { const userInput = (await askQuestion('You: ')).trim();
if (userInput.toLowerCase() === 'exit' || userInput.toLowerCase() === 'quit') { rl.close(); break; }
if (!userInput) { continue; }
try { const response = await client.agents.messages.create(agentId, { messages: [{ role: 'user', content: userInput }] });
for (const message of response.messages) { if (message.message_type === 'assistant_message') { console.log(`\nAssistant: ${(message as any).content}\n`); } } } catch (error) { console.error(`Error: ${error}\n`); } }}
main().catch(console.error);import osfrom letta_client import Lettafrom dotenv import load_dotenv
load_dotenv()
def main(): letta_api_key = os.getenv("LETTA_API_KEY") if not letta_api_key: print("Error: LETTA_API_KEY not found") return
letta_client = Letta(api_key=letta_api_key)
AGENT_ID = input("Enter your agent ID: ").strip() if not AGENT_ID: print("Error: Agent ID required") return
print("\nGraphiti Memory Assistant") print("Type 'exit' to quit\n")
while True: user_input = input("You: ").strip()
if user_input.lower() in ['exit', 'quit']: break
if not user_input: continue
try: response = letta_client.agents.messages.create( agent_id=AGENT_ID, messages=[{"role": "user", "content": user_input}] )
for message in response.messages: if message.message_type == 'assistant_message': print(f"\nAssistant: {message.content}\n")
except Exception as e: print(f"Error: {str(e)}\n")
if __name__ == "__main__": main()import Letta from '@letta-ai/letta-client';import * as dotenv from 'dotenv';import * as readline from 'readline';
dotenv.config();
async function main() { const lettaApiKey = process.env.LETTA_API_KEY; if (!lettaApiKey) { console.error('Error: LETTA_API_KEY not found'); return; }
const rl = readline.createInterface({ input: process.stdin, output: process.stdout });
const askQuestion = (query: string): Promise<string> => { return new Promise((resolve) => { rl.question(query, resolve); }); };
const agentId = (await askQuestion('Enter your agent ID: ')).trim(); if (!agentId) { console.error('Error: Agent ID required'); rl.close(); return; }
const client = new Letta({ apiKey: lettaApiKey });
console.log('\nGraphiti Memory Assistant'); console.log("Type 'exit' to quit\n");
while (true) { const userInput = (await askQuestion('You: ')).trim();
if (userInput.toLowerCase() === 'exit' || userInput.toLowerCase() === 'quit') { rl.close(); break; }
if (!userInput) { continue; }
try { const response = await client.agents.messages.create(agentId, { messages: [{ role: 'user', content: userInput }] });
for (const message of response.messages) { if (message.message_type === 'assistant_message') { console.log(`\nAssistant: ${(message as any).content}\n`); } } } catch (error) { console.error(`Error: ${error}\n`); } }}
main().catch(console.error);import osfrom letta_client import Lettafrom dotenv import load_dotenv
load_dotenv()
def main(): letta_api_key = os.getenv("LETTA_API_KEY") if not letta_api_key: print("Error: LETTA_API_KEY not found") return
letta_client = Letta(api_key=letta_api_key)
AGENT_ID = input("Enter your agent ID: ").strip() if not AGENT_ID: print("Error: Agent ID required") return
print("\nWeaviate Memory Assistant") print("Type 'exit' to quit\n")
while True: user_input = input("You: ").strip()
if user_input.lower() in ['exit', 'quit']: break
if not user_input: continue
try: response = letta_client.agents.messages.create( agent_id=AGENT_ID, messages=[{"role": "user", "content": user_input}] )
for message in response.messages: if message.message_type == 'assistant_message': print(f"\nAssistant: {message.content}\n")
except Exception as e: print(f"Error: {str(e)}\n")
if __name__ == "__main__": main()import Letta from '@letta-ai/letta-client';import * as dotenv from 'dotenv';import * as readline from 'readline';
dotenv.config();
async function main() { const lettaApiKey = process.env.LETTA_API_KEY; if (!lettaApiKey) { console.error('Error: LETTA_API_KEY not found'); return; }
const rl = readline.createInterface({ input: process.stdin, output: process.stdout });
const askQuestion = (query: string): Promise<string> => { return new Promise((resolve) => { rl.question(query, resolve); }); };
const agentId = (await askQuestion('Enter your agent ID: ')).trim(); if (!agentId) { console.error('Error: Agent ID required'); rl.close(); return; }
const client = new Letta({ apiKey: lettaApiKey });
console.log('\nWeaviate Memory Assistant'); console.log("Type 'exit' to quit\n");
while (true) { const userInput = (await askQuestion('You: ')).trim();
if (userInput.toLowerCase() === 'exit' || userInput.toLowerCase() === 'quit') { rl.close(); break; }
if (!userInput) { continue; }
try { const response = await client.agents.messages.create(agentId, { messages: [{ role: 'user', content: userInput }] });
for (const message of response.messages) { if (message.message_type === 'assistant_message') { console.log(`\nAssistant: ${(message as any).content}\n`); } } } catch (error) { console.error(`Error: ${error}\n`); } }}
main().catch(console.error);import osfrom letta_client import Lettafrom dotenv import load_dotenv
load_dotenv()
def main(): letta_api_key = os.getenv("LETTA_API_KEY") if not letta_api_key: print("Error: LETTA_API_KEY not found") return
letta_client = Letta(api_key=letta_api_key)
AGENT_ID = input("Enter your agent ID: ").strip() if not AGENT_ID: print("Error: Agent ID required") return
print("\nMem0 Memory Assistant") print("Type 'exit' to quit\n")
while True: user_input = input("You: ").strip()
if user_input.lower() in ['exit', 'quit']: break
if not user_input: continue
try: response = letta_client.agents.messages.create( agent_id=AGENT_ID, messages=[{"role": "user", "content": user_input}] )
for message in response.messages: if message.message_type == 'assistant_message': print(f"\nAssistant: {message.content}\n")
except Exception as e: print(f"Error: {str(e)}\n")
if __name__ == "__main__": main()import Letta from '@letta-ai/letta-client';import * as dotenv from 'dotenv';import * as readline from 'readline';
dotenv.config();
async function main() { const lettaApiKey = process.env.LETTA_API_KEY; if (!lettaApiKey) { console.error('Error: LETTA_API_KEY not found'); return; }
const rl = readline.createInterface({ input: process.stdin, output: process.stdout });
const askQuestion = (query: string): Promise<string> => { return new Promise((resolve) => { rl.question(query, resolve); }); };
const agentId = (await askQuestion('Enter your agent ID: ')).trim(); if (!agentId) { console.error('Error: Agent ID required'); rl.close(); return; }
const client = new Letta({ apiKey: lettaApiKey });
console.log('\nMem0 Memory Assistant'); console.log("Type 'exit' to quit\n");
while (true) { const userInput = (await askQuestion('You: ')).trim();
if (userInput.toLowerCase() === 'exit' || userInput.toLowerCase() === 'quit') { rl.close(); break; }
if (!userInput) { continue; }
try { const response = await client.agents.messages.create(agentId, { messages: [{ role: 'user', content: userInput }] });
for (const message of response.messages) { if (message.message_type === 'assistant_message') { console.log(`\nAssistant: ${(message as any).content}\n`); } } } catch (error) { console.error(`Error: ${error}\n`); } }}
main().catch(console.error);import osfrom letta_client import Lettafrom dotenv import load_dotenv
load_dotenv()
def main(): letta_api_key = os.getenv("LETTA_API_KEY") if not letta_api_key: print("Error: LETTA_API_KEY not found") return
letta_client = Letta(api_key=letta_api_key)
AGENT_ID = input("Enter your agent ID: ").strip() if not AGENT_ID: print("Error: Agent ID required") return
print("\nZep Memory Assistant") print("Type 'exit' to quit\n")
while True: user_input = input("You: ").strip()
if user_input.lower() in ['exit', 'quit']: break
if not user_input: continue
try: response = letta_client.agents.messages.create( agent_id=AGENT_ID, messages=[{"role": "user", "content": user_input}] )
for message in response.messages: if message.message_type == 'assistant_message': print(f"\nAssistant: {message.content}\n")
except Exception as e: print(f"Error: {str(e)}\n")
if __name__ == "__main__": main()import Letta from '@letta-ai/letta-client';import * as dotenv from 'dotenv';import * as readline from 'readline';
dotenv.config();
async function main() { const lettaApiKey = process.env.LETTA_API_KEY; if (!lettaApiKey) { console.error('Error: LETTA_API_KEY not found'); return; }
const rl = readline.createInterface({ input: process.stdin, output: process.stdout });
const askQuestion = (query: string): Promise<string> => { return new Promise((resolve) => { rl.question(query, resolve); }); };
const agentId = (await askQuestion('Enter your agent ID: ')).trim(); if (!agentId) { console.error('Error: Agent ID required'); rl.close(); return; }
const client = new Letta({ apiKey: lettaApiKey });
console.log('\nZep Memory Assistant'); console.log("Type 'exit' to quit\n");
while (true) { const userInput = (await askQuestion('You: ')).trim();
if (userInput.toLowerCase() === 'exit' || userInput.toLowerCase() === 'quit') { rl.close(); break; }
if (!userInput) { continue; }
try { const response = await client.agents.messages.create(agentId, { messages: [{ role: 'user', content: userInput }] });
for (const message of response.messages) { if (message.message_type === 'assistant_message') { console.log(`\nAssistant: ${(message as any).content}\n`); } } } catch (error) { console.error(`Error: ${error}\n`); } }}
main().catch(console.error);Run the chat script with your agent ID:
python chat.pynpx tsx chat.tsTry these example conversations to test memory functionality:
First conversation:
You: My name is James and I love Python programmingAssistant: Nice to meet you, James! I've stored that you love Python programming...
You: I'm working on a machine learning projectAssistant: That's exciting! I've noted that you're working on a machine learning project...Second conversation (new session):
You: What do you remember about me?Assistant: Let me search my memories... You're James, and you love Python programming. You're also working on a machine learning project.The agent stores memories in your external database and retrieves them across sessions, demonstrating persistent memory storage.
You can inspect your agent’s behavior and see the memory tool calls in the Letta Agent Development Environment (ADE):
Navigate to the ADE
Log in to letta.com and click on Agents in the sidebar to view your agents.
Open your agent
Click Open in ADE on your agent to open it in the playground.
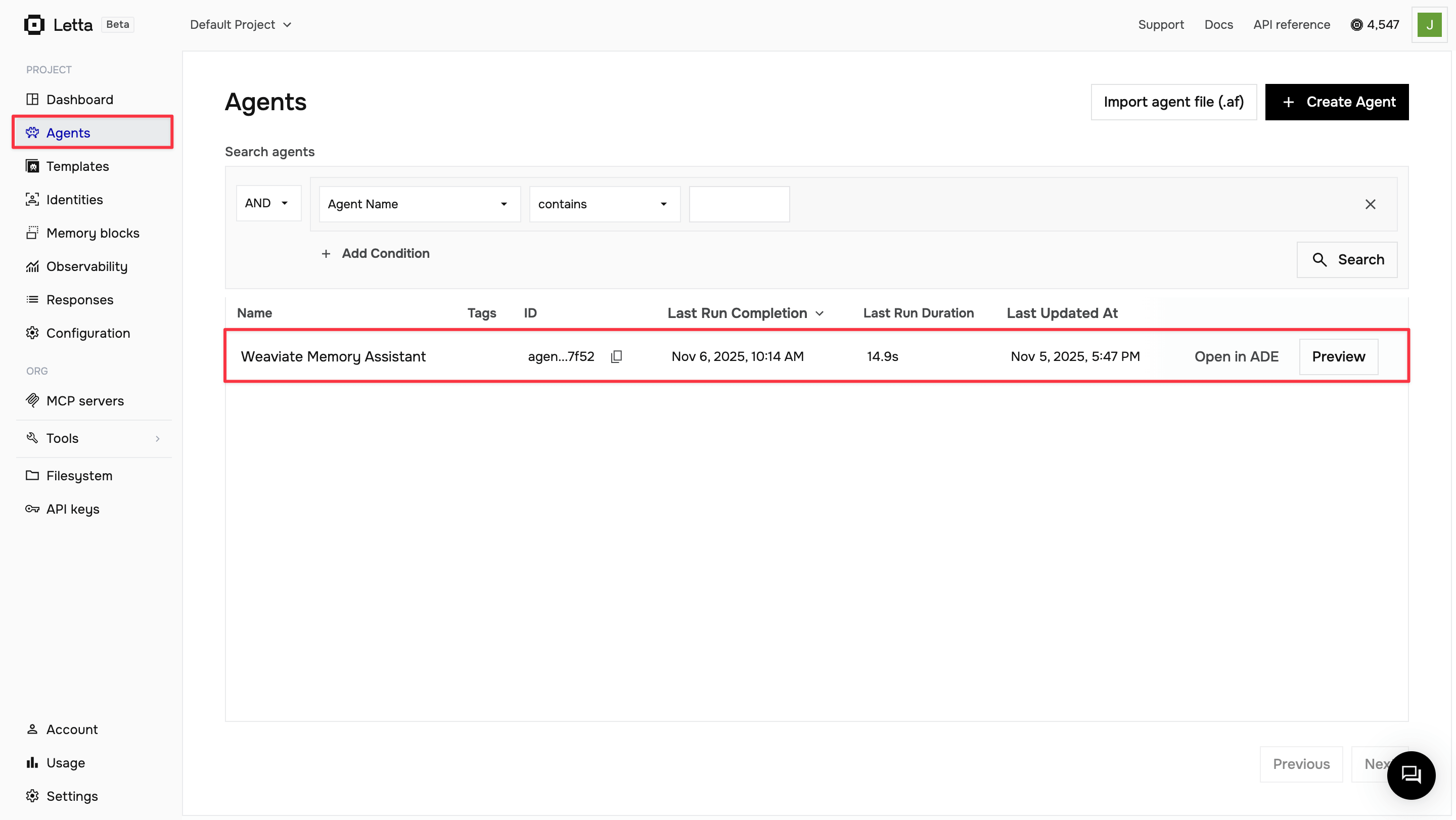
View tool calls
As you chat with your agent, expand the message details to see the tool calls being made. You’ll see when the agent calls insert_memory to store information and when it calls your provider’s search function to retrieve memories.
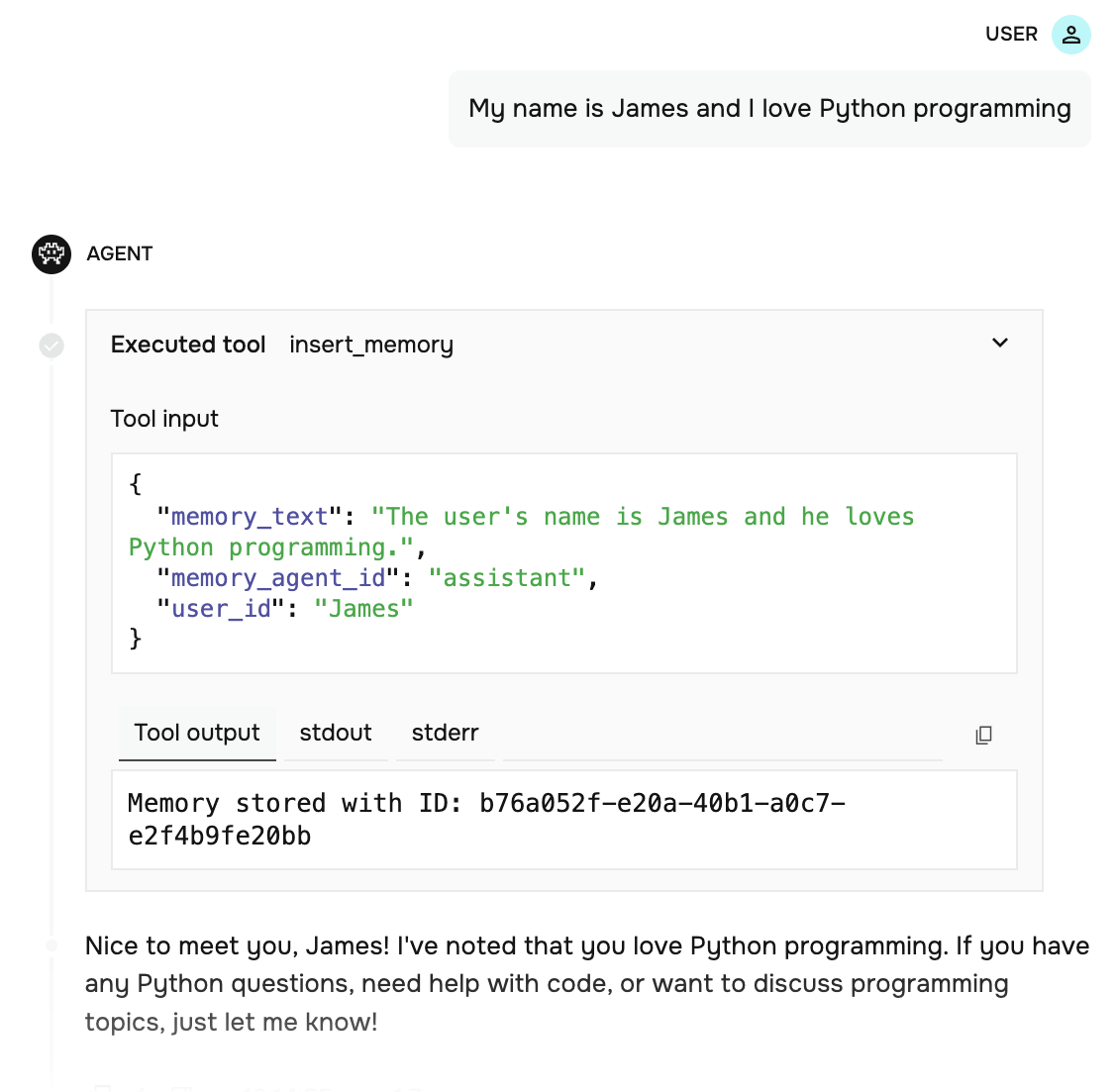
The ADE provides visibility into your agent’s decision-making process, showing you exactly when and how it uses your custom memory tools.
Now that you’ve integrated external memory storage with Letta, you can expand on this foundation:
Custom tools
Learn more about creating custom tools for your agents.
Agent configuration
Explore advanced agent configuration options.
RAG with Letta
Build retrieval-augmented generation systems with Letta.
Multi-agent systems
Create systems with multiple specialized agents.